Quick Summary
- Choose naturally resistant woods like cedar or redwood
- Prepare the ground by removing debris and ensuring proper drainage
- Create a barrier using gravel or a plastic liner
- Apply protective coatings like water-repellent sealant or wood preservative
Choose the Right Type of Wood
Choosing the right type of wood is crucial in preventing rot, as certain woods are naturally more resistant to moisture and decay. When it comes to selecting wood for ground contact, there are a few key factors to consider. First, you should opt for woods that have a natural resistance to rot, such as cedar or redwood. These types of wood contain natural oils and chemicals that act as a barrier against moisture and decay. Additionally, choosing alternative materials like composite lumber or pressure-treated wood can also help prevent rot. Composite lumber is made from a combination of wood fibers and recycled plastic, making it highly resistant to rot and decay. Pressure-treated wood, on the other hand, is infused with chemicals that protect it from rot and insect damage. Understanding wood preservation techniques is also essential in preventing rot. Applying a wood preservative or sealant can provide an extra layer of protection against moisture and decay. Regularly inspecting and maintaining the wood, such as keeping it clean and free from standing water, can also help prolong its lifespan. By choosing the right type of wood and implementing proper wood preservation techniques, you can effectively prevent rot and ensure the longevity of your wood in the ground.Prepare the Ground
Before starting, it’s important to ensure the ground is well-prepared to protect your wooden structures. Preparing the soil is crucial in preventing wood from rotting in the ground. Start by clearing the area of any debris, rocks, or plants that may obstruct proper drainage. Make sure the soil is level and free from any excess moisture, as water can lead to rotting. Next, consider using gravel as a base for your wooden structures. Gravel provides excellent drainage, allowing water to flow away from the wood and preventing it from becoming saturated. Lay a layer of gravel evenly across the ground, ensuring it is compacted and level. This will create a stable foundation for your wooden structures and help to keep them dry. Remember to choose a size of gravel that is appropriate for your project, as larger stones may provide better drainage. By preparing the ground properly and using gravel as a base, you can protect your wooden structures from rot and ensure their longevity.Create a Barrier
To make sure your wooden structures stay in top shape, it’s essential to create a barrier that shields them from potential damage. When it comes to preventing wood from rotting in the ground, proper ground preparation and selecting suitable barriers are crucial steps to take. First, before installing any wooden structure, you must prepare the ground properly. Start by clearing the area of any debris, rocks, or weeds that could potentially trap moisture against the wood. Level the ground and ensure proper drainage by grading it away from the structure. This will help prevent water from pooling around the wood, which can lead to rotting.
Next, it’s time to select suitable barriers to protect your wood. One effective option is using pressure-treated wood, which has been chemically treated to resist rot and decay. Another option is using a waterproofing membrane, such as a rubber or plastic sheet, to create a protective barrier between the wood and the ground. Additionally, you can consider using concrete footings or metal brackets to elevate the wood off the ground, further preventing moisture absorption.
By following these steps and taking the necessary precautions, you can ensure that your wooden structures are shielded from potential damage caused by rotting in the ground. Remember, proper ground preparation and selecting suitable barriers are key to maintaining the longevity and safety of your wooden structures.
First, before installing any wooden structure, you must prepare the ground properly. Start by clearing the area of any debris, rocks, or weeds that could potentially trap moisture against the wood. Level the ground and ensure proper drainage by grading it away from the structure. This will help prevent water from pooling around the wood, which can lead to rotting.
Next, it’s time to select suitable barriers to protect your wood. One effective option is using pressure-treated wood, which has been chemically treated to resist rot and decay. Another option is using a waterproofing membrane, such as a rubber or plastic sheet, to create a protective barrier between the wood and the ground. Additionally, you can consider using concrete footings or metal brackets to elevate the wood off the ground, further preventing moisture absorption.
By following these steps and taking the necessary precautions, you can ensure that your wooden structures are shielded from potential damage caused by rotting in the ground. Remember, proper ground preparation and selecting suitable barriers are key to maintaining the longevity and safety of your wooden structures.
Apply Protective Coatings
To protect your wood from rotting in the ground, there are a few key points to consider. First, using waterproof sealants or paints can create a barrier that prevents moisture from seeping into the wood.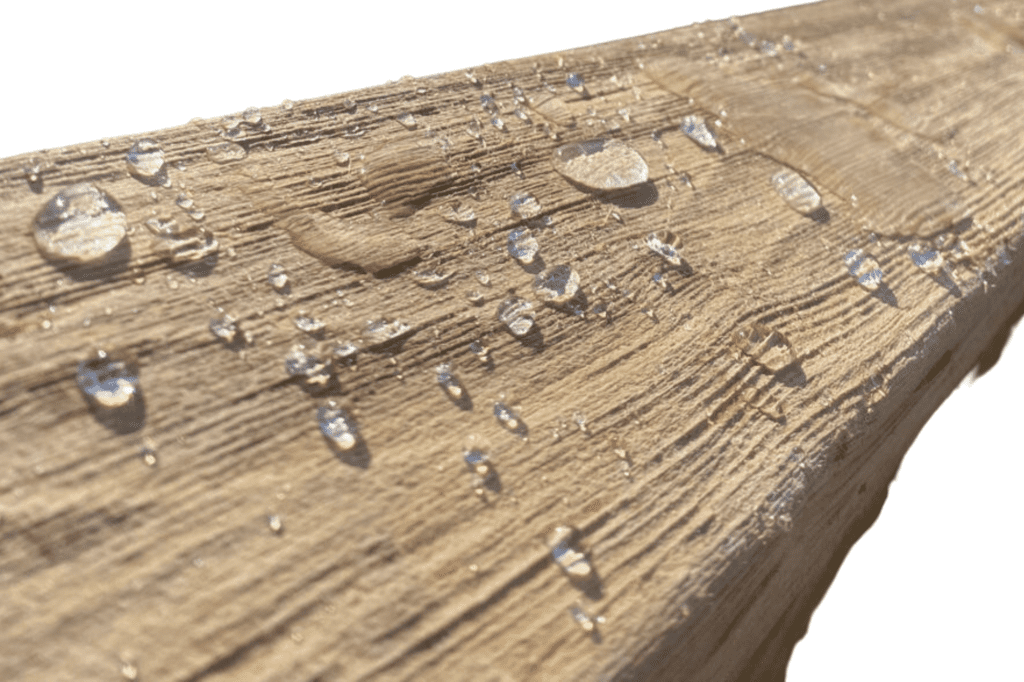 Second, applying wood stains or oils can add an extra layer of protection against water damage.
Lastly, it’s important to remember to regularly maintain and reapply these protective coatings to ensure long-lasting results.
Second, applying wood stains or oils can add an extra layer of protection against water damage.
Lastly, it’s important to remember to regularly maintain and reapply these protective coatings to ensure long-lasting results.
Using Waterproof Sealants or Paints
One effective way of protecting wood from rotting in the ground is by using waterproof sealants or paints. These can create a barrier against moisture, preventing it from seeping into the wood and causing rot. When considering which option to use, it’s important to weigh the pros and cons of using sealants versus paints. In the table below, you can compare the characteristics of waterproof sealants and paints:| Waterproof Sealants | Paints | |
|---|---|---|
| Pros | – Excellent moisture protection |
- Can penetrate wood for deeper protection
- UV resistance
- Flexible, allowing for wood expansion and contraction | – Wide variety of colors and finishes
- Easy application
- Can enhance the appearance of wood | |Cons| – May alter the natural look of wood
- Can be more expensive
- Requires reapplication over time | – Less effective at deep penetration
- May crack or peel over time
- Limited moisture protection |
Applying Wood Stains or Oils
Applying wood stains or oils can significantly enhance the natural beauty and durability of the wood, providing long-lasting protection against moisture and rot. Here are three key benefits of using wood stains or oils:- Moisture Resistance: Wood stains or oils create a protective barrier that prevents water from seeping into the wood, reducing the chances of rotting and warping.
- UV Protection: Stains or oils with UV filters shield the wood from harmful sun rays, preventing discoloration and fading over time.
- Enhanced Aesthetic Appeal: Wood stains penetrate deep into the wood, highlighting the natural grain and adding depth to its appearance. Oils, on the other hand, provide a rich, glossy finish that enhances the wood’s beauty while offering protection.
Elevate the Wood
Elevating the wood above the ground will help prevent it from rotting and extend its lifespan. When you raise the wood, you create a barrier between the ground and the wood, reducing its exposure to moisture and preventing rot. One way to raise the wood is by using treated wood, which is specially designed to withstand moisture and decay. Treated wood is treated with chemicals that make it resistant to rot, insects, and fungi. By using treated wood, you can ensure that your wood is protected from the elements and will last longer. In addition to using treated wood, you can also use other methods to elevate the wood. One option is to place the wood on concrete or stone blocks, creating a sturdy foundation that keeps it off the ground. Another option is to use metal or plastic brackets to elevate the wood, creating space between the ground and the wood. This allows air to circulate and reduces the chances of rotting. When elevating the wood, make sure to choose a level and stable surface. Uneven surfaces can cause the wood to shift and become unstable, increasing the risk of accidents. Additionally, regularly check the wood for any signs of decay or damage and replace any compromised pieces promptly. By taking these precautions and elevating the wood, you can ensure its longevity and keep yourself and others safe.Which Grass Type, St Augustine or Zoysia, is More Resistant to Rotting in the Ground?
The ultimate grass showdown guide tackles the question of which grass type, St Augustine or Zoysia, is more resistant to rotting in the ground. Both grasses have their strengths, but in terms of rot resistance, Zoysia edges ahead. Its dense thatch and ability to withstand excessive moisture make it less susceptible to rotting compared to St Augustine.
Maintain Proper Ventilation
To ensure the longevity of your elevated wood structure, it’s crucial to maintain proper ventilation. Proper air circulation is essential for preventing moisture buildup, which can lead to rot and decay. Here are five important steps to improve air circulation and control moisture:- Install vents: Place vents in strategic locations around your elevated wood structure. These vents allow air to flow freely, preventing stagnant pockets of moisture that can lead to rot.
- Use breathable materials: Opt for breathable materials such as lattice or slatted panels when constructing your elevated wood structure. These materials allow air to pass through, promoting better ventilation and reducing the risk of rot.
- Keep the area around the structure clear: Ensure that there are no obstructions blocking the airflow around your wood structure. Trim back vegetation and remove any debris that may impede proper ventilation.
- Regularly inspect for blockages: Regularly check your vents and ensure they are not blocked by dirt, leaves, or other debris. Clear any blockages to maintain proper airflow and prevent moisture buildup.
- Monitor humidity levels: Use a moisture meter to monitor the moisture levels in and around your elevated wood structure. If levels are consistently high, consider using a dehumidifier to remove excess moisture from the air.
Regularly Inspect and Repair
Regularly inspect and repair your wood to ensure its longevity. Check for signs of decay or damage, such as discoloration, soft spots, or crumbling wood. If you find rotted wood, treat and repair it promptly by removing the affected areas and filling them with wood filler or epoxy. By staying proactive in your maintenance routine, you can prevent further damage and extend the life of your wood.Checking for Signs of Decay or Damage
Inspecting the wood for any indications of decay or damage is an essential step in preventing rot in the ground. By regularly checking for signs of decay or damage, you can take immediate action to repair any issues and prevent further deterioration. Start by looking for soft spots, discoloration, or crumbling wood, as these are clear indicators of decay. If you notice any damage, such as cracks or splits, it’s important to repair them promptly to prevent moisture from seeping in and causing rot. Additionally, be on the lookout for termite infestation, as these pests can quickly destroy wood. Look for small holes, sawdust-like droppings, or mud tubes, and take appropriate measures to prevent or eradicate termites. By staying vigilant and addressing any issues promptly, you can effectively protect your wood from rot and ensure its longevity in the ground.Treating and Repairing Rotted Wood
Make sure you treat and repair any rotted wood you find to prevent further damage and extend the lifespan of your wooden structures. Here are some steps to effectively treat and repair rotted wood, preventing wood decay:- Start by removing any loose or decayed wood using a chisel or scraper.
- Apply a wood hardener or consolidant to strengthen the remaining wood and prevent further decay.
- Sand the repaired area to achieve a smooth finish and blend it with the surrounding wood.
- Finally, apply a wood preservative or primer to protect the repaired wood from future rot.









