Overwhelmed by invasive blackberry plants taking over your garden? Worry no more, because this comprehensive guide offers eco-friendly gardening tips and natural overrun solutions that put an end to blackberry domination. We will uncover the secrets of plant-based blackberry suppression and blackberry eradication techniques that will rejuvenate your garden space and bring balance and harmony to your outdoor oasis.
Understanding the biology of blackberries is essential for successfully curbing their aggressive growth without relying on traditional chemical treatments. By employing the power of specific plants, natural predators, and physical barriers, you can triumph over blackberry infestations with ease.
Key Takeaways
- Discover effective, sustainable methods for invasive blackberry control to preserve the health of your garden
- Learn how to use aggressive plants and animals to outcompete blackberries and revitalize your garden
- Explore smothering techniques and physical barriers that can halt blackberry growth in its tracks
- Understand the importance of companion planting and choosing the right plants to combat and suppress blackberries
- Find out how goats can serve as natural predators and allies in the fight against blackberry overgrowth
Understanding Blackberry Invasion in Your Garden
The common weedy Himalayan blackberry in the Pacific Northwest, also known as Rubus discolor, originates from Europe and is notorious for its resilience and aggression, forming impenetrable thickets. This blackberry variety thrives in moist, disturbed areas and rapidly expands through long canes that can root upon soil contact. Understanding this plant’s life cycle and aggressive nature is essential for effective removal.
Choosing a blackberry removal strategy should align with the goal of reintroducing desired plants to the area. Consistent and persistent manual removal, planting of competing vegetation, and utilizing animals for grazing can lead to successful eradication without the need for harmful herbicides. Familiarize yourself with the phases of blackberry plant biology to more effectively manage this invasive species:
| Phase | Description |
|---|---|
| Germination | Blackberry seeds require exposure to cold temperatures followed by warm soil to germinate. |
| Growth | Long canes or stems, covered in thorns, grow rapidly and can root at the tip upon contact with soil. Canes can grow up to 20 feet in length, smothering and shading out surrounding vegetation. |
| Reproduction | Clusters of white or pink flowers form on the canes, eventually producing the characteristic aggregate fruit made up of multiple small drupelets. New growth also takes place via root suckers. |
| Dispersal | Animals, particularly birds, consume the fruit and naturally disperse the seeds, promoting the spread of the invasive plant. |
To control the garden overgrowth caused by invasive blackberry plants, an understanding of invasive species management tactics is essential. The following methods have proven to be effective in controlling blackberry invasion:
- Manual removal: Regularly cut back the canes, dig up the root system, and dispose of plant material to avoid regrowth.
- Competing vegetation: Plant vigorous species, such as artichokes, asparagus, or certain wildflower species, to compete for nutrients and light with the blackberry plants.
- Grazing animals: Employ goats and other herbivores to graze on blackberry plants and assist in controlling overgrowth.
By incorporating habits to control blackberry invasion and garden overgrowth in your landscaping routine, you can effectively manage the spread of this invasive species and protect your garden’s biodiversity.
Physical Barriers: Using Smothering Techniques Effectively
One effective method for controlling invasive blackberries is through the use of smothering techniques. By employing physical barriers such as EPDM barriers and cardboard layers, you can prevent blackberry sprouts from growing while supporting natural suppression methods and contributing to overall soil health.
The Role of EPDM and Cardboard Layers in Controlling Blackberries
EPDM barriers, made of rubber membranes, and thick cardboard layers can be used to create a light-blocking barrier around invasive blackberry plants. This organic suppression strategy works by cutting off the plants’ access to sunlight, ultimately inhibiting their growth. Triple-thick cardboard is particularly effective due to its ability to break down into the soil and support the colonization of fungi, further contributing to soil health and natural blackberry control.
Creating a Surround Barrier with Wood Chips and Compost
In addition to smothering techniques, creating a surround barrier is another effective method of blackberry control. This strategy involves excavating a trench around the blackberry patch and filling it with a combination of wood chips and larger pieces of wood. By doing so, you essentially create a buried “wood doughnut” which serves as a natural blackberry fencing while also supporting soil health through aeration.
- Excavate a trench surrounding the blackberry patch.
- Fill the trench with a mix of wood chips and larger wood pieces, forming a dense barrier.
- Cover the wood-filled trench with topsoil, creating a barrier that prevents the spread of blackberry plants and makes seedling removal more straightforward.
This method not only contains the invasive plants but also promotes overall garden health, even in areas susceptible to drought conditions. By using wood chip barriers and compost moats in conjunction with EPDM barriers and cardboard layers, you create an effective, multifaceted approach to controlling and suppressing invasive blackberries using eco-friendly, natural suppression methods.
The Importance of Companion Planting Against Blackberries
Companion planting is a powerful technique that leverages the natural relationships between plants to enhance garden health and productivity. Implemented correctly, this approach can play a significant role in promoting garden biodiversity and strengthening crop interactions. By selecting the right or wrong plant companions for blackberries, you can greatly impact fruit yield and overall garden biodiversity.
There are specific plants known for their vigor that can compete intensely with blackberries for nutrients, ultimately overcrowding and overshadowing them. However, suitable companion plants can help suppress blackberries and bring balance to your garden eco-system. In this section, we’ll discuss some effective plant choices and permaculture design techniques that boost plant companionship while reducing blackberry growth.
| Plant | Vigor | Effect on Blackberries |
|---|---|---|
| Artichokes | High | Competes for nutrients, overcrowds and overshadows blackberries |
| Asparagus | High | Competes for nutrients, overcrowds and overshadows blackberries |
| Oregano | Moderate | Suppression when used in moderation |
Artichokes and asparagus are two vigorous plants known for their ability to compete with and overshadow blackberry plants. They absorb essential nutrients and dominate the surrounding space, limiting the potential for blackberry growth. By incorporating these plants into your garden design, you can effectively suppress blackberries and bolster garden biodiversity.
On the other hand, oregano offers a more moderated approach to blackberry suppression. Its aggressive spreading nature can help suppress blackberries when used in appropriate quantities. By carefully planning the distribution of your plant choices, you can strengthen crop interactions and garden biodiversity while keeping blackberry growth in check.
To summarize, selecting the right combination of companion plants is crucial for managing blackberry invasions and enhancing overall garden health. Striking a balance between vigorous competitors and plants that offer moderate suppression is key to ensuring a diverse and productive eco-system without resorting to chemicals.
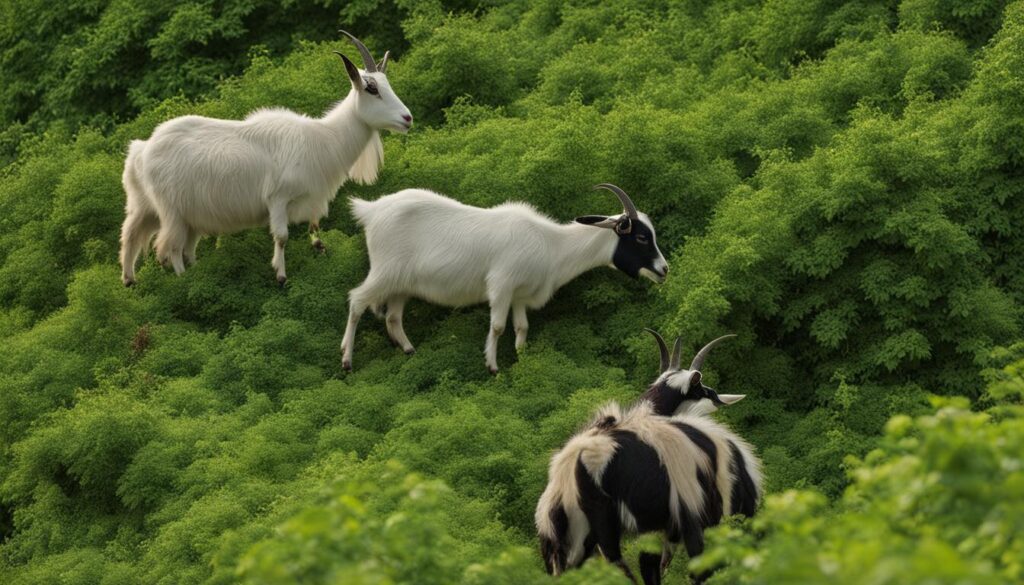
Natural Predators: How Goats Can Help Manage Blackberry Overgrowth
One possible solution to the problem of blackberry overgrowth comes in the form of an unlikely ally: goats. As natural blackberry predators, goats have been used as a landscaping tool to control invasive species in several parts of the world, including Australia and New Zealand. These remarkable animals are not only adept at goat grazing on blackberries, but they also provide a number of biological control methods to help achieve sustainable blackberry removal.
Goats have evolved to digest a wide variety of plants, but they show a particular preference for blackberries. This makes them a valuable resource for landowners struggling to control the rapid spread of invasive species like the Himalayan blackberry. By consistently and persistently grazing on blackberry bushes, goats can clear large areas of infested land and help prevent regrowth.
There are several advantages to using goats for blackberry management instead of relying on chemical herbicides. Some of these benefits include:
- Reduced use of chemicals, promoting a healthier environment and ecosystem
- Lower costs associated with herbicide applications and labor-intensive manual removal
- Minimized soil disturbance, which fosters better conditions for native plants to thrive
- An opportunity for landowners to participate in responsible, eco-friendly land management practices
Goats can be particularly effective in managing blackberry overgrowth in larger pastures and natural areas designated for firebreaks, wildlife habitat restoration, or other conservation efforts. Their innate ability to graze on a wide range of invasive plants, along with their low environmental impact, makes them an attractive option for landowners seeking a sustainable and environmentally friendly solution to blackberry control.
Ultimately, by enlisting the help of an ancient and natural predator like goats, you can effectively manage blackberry overgrowth while reducing your reliance on chemicals and labor-intensive removal methods. In doing so, you’ll be supporting a healthier ecosystem that is better equipped to thrive without the intrusive presence of invasive blackberries.
Integrating Oregano and Mint to Suppress Unwanted Blackberry Plants
One of the most effective ways to achieve natural blackberry control is through integrating aggressive growers like oregano and mint into your garden. These plants can outcompete and suppress blackberries without the need for harsh chemical herbicides. Explore the herbaceous control methods that oregano and mint possess to minimize invasive species and enjoy the aromatic herb benefits they provide.
Utilizing Oregano’s Aggressive Growing Habits
Oregano, a popular herb known for its distinct flavor and aroma, can be a powerful ally in the fight against invasive blackberry plants. Its rapid growth and expansive nature allow it to effectively compete against blackberries for valuable resources like space, light, and nutrients.
To successfully use oregano as a blackberry suppressant, plant it strategically in areas where blackberries are known to thrive. Ensure that the oregano is provided with adequate sunlight and nutrients to maintain its aggressive growth, naturally overtaking and suppressing the unwanted blackberries.
Exploring Mint Varieties for Blackberry Control
Mint plants, with their refreshing aroma and vigorous growth habits, can also be used in the battle against invasive blackberries. There are numerous mint varieties beyond the traditional peppermint and spearmint, each possessing unique characteristics that can aid in blackberry control.
- Peppermint (Mentha x piperita) – An aromatic variety with strong flavor and scent, excellent for deterring pests and competing with blackberries for resources.
- Spearmint (Mentha spicata) – A milder variety that grows quickly and can form dense mats, potentially smothering blackberry plants.
- Chocolate mint (Mentha x piperita ‘Chocolate’) – A distinctive variety with a subtle chocolate scent, it can be utilized for its aggressive growth and to add diversity to the garden.
Take advantage of the invasive species suppression capabilities of these mint varieties by planting them in problem areas of the garden or around the perimeter to create a barrier that prevents blackberries from spreading.
Both oregano and mint offer effective, natural blackberry remedies that can hinder the spread of these invasive plants. By embracing their aggressive growing nature and understanding how to deploy these herbs in a strategic manner, it is possible to keep blackberries at bay while enjoying the array of aromatic herb benefits they provide.
Favorable Plants vs. Blackberries: Which Ones Are Battle-Ready?
Identifying plants that can withstand blackberry aggression or even suppress their growth is key to reclaiming your garden. Strategically chosen plants are ‘battle-ready’ and can effectively coexist with or outcompete blackberries, allowing gardeners to maintain a diverse and productive ecosystem without resorting to chemicals.
When it comes to blackberry competition, several species stand out as favorable flora in garden planning for invasive species resistance. We’ve curated a list of some stellar plants to help you ward off blackberries and revitalize your garden:
- Asparagus (Asparagus officinalis): The robust root system of asparagus helps it persist against blackberries, offering shade to impede their growth. Since blackberries prefer sunlight over shade, asparagus can stunt their growth while providing a delicious and nutritious harvest.
- Artichoke (Cynara cardunculus): Artichokes are large plants well-known for pushing invasive plants like blackberries out as they grow. Their impressive stature enables them to outcompete blackberries and protect vulnerable surrounding plants from the invasive species.
- Oregon Grape (Mahonia aquifolium): As a native plant to the Pacific Northwest, Oregon grape offers an ideal alternative to invasive blackberries. Oregon grape’s holly-like foliage creates an unwelcoming environment for blackberries to thrive, thwarting their aggressive habits.
- Evergreen Huckleberry (Vaccinium ovatum): A native shrub that provides beautiful foliage and delicious fruit, evergreen huckleberry thrives under the canopy of tall trees. This shade tolerance allows it to compete with blackberries that prefer brighter areas.
Consider integrating these battle-ready plants into your garden to gain the upper hand against invasive blackberries. In practice, implementation of well-considered plant strategies can outshine chemical treatments, counteracting blackberry growth and cultivating a healthy, thriving garden ecosystem.
How to Revitalize Your Garden Post-Blackberry Eradication
Once you have successfully removed blackberries from your garden, the focus shifts to garden revitalization and rehabilitation. Choosing the right plants to reintroduce to the area is critical in ensuring sustainable garden health and resilience against further invasions. Native species often prove to be the most effective in post-eradication planting, as they can seamlessly fill the void left by the invasive blackberry plants and align with desired ecological outcomes.
Choosing the Right Plants for Garden Rehabilitation
Some key factors to consider when selecting suitable plants for garden rehabilitation include:
- The preferred environmental conditions of the chosen plants, such as sunlight, soil type, and moisture and nutrient requirements.
- Compatibility with existing plant species in the garden, ensuring harmony among the garden community.
- The growth habits and maintenance needs of the chosen plants, which should align with your gardening goals and abilities.
It is also essential to prioritize native plants that support local wildlife and ecosystems. These plants have evolved to coexist with the area’s native birds, insects, and other flora, making them an integral part of the delicate balance that constitutes a healthy garden.
Some notable native plants to consider for post-blackberry eradication garden revival include:
| Plant | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Redtwig Dogwood (Cornus sericea) | A native deciduous shrub with bright red stems. | Provides food and habitat for birds; effectively fills spaces vacated by blackberries. |
| Tall Oregon Grape (Mahonia aquifolium) | An evergreen shrub with holly-like leaves and clusters of fragrant yellow flowers. | Attracts pollinators and supports birds with its berries; forms dense thickets to crowd out invasive species. |
| Western Sword Fern (Polystichum munitum) | Large, hardy fern with bright green fronds. | Provides ground cover and habitat for wildlife; decomposing fronds create organic matter to enrich the soil. |
| Mock Orange (Philadelphus lewisii) | A native deciduous shrub with fragrant white flowers. | Supports beneficial insects and pollinators; adds fragrance and visual appeal to the garden. |
By considering factors such as environmental preferences, compatibility, and maintenance, you can effectively revitalize your garden after blackberry eradication, ensuring the long-term success of garden rehabilitation and ecological restoration.
How Can I Naturally Control Blackberry Overgrowth Without Using Chemicals Like Roundup?
If you’re looking for natural ways to control blackberry overgrowth without using chemicals like Roundup, consider using physical methods like hand-pulling or cutting the bushes. Another option is to smother the bushes with a thick layer of mulch to restrict their growth without the negative effects of Roundup on blackberry bushes.
Conclusion
In summary, successfully managing and eliminating invasive blackberries from your garden is achievable through a combination of effective, eco-friendly strategies. Armed with the essential knowledge of blackberry biology, you can make informed decisions and take action to overcome blackberry infestations while promoting sustainable gardening practices.
By employing techniques such as physical barriers, strategic companion planting, and utilizing natural predators like goats, you can regain control over your green spaces. In turn, this fosters a biodiverse, harmonious environment while minimizing negative environmental impacts. This holistic approach to blackberry removal success emphasizes environmentally-conscious landscaping and natural plant solutions, empowering you to manage your garden more responsibly and efficiently.
Ultimately, nurturing a thriving outdoor space while keeping invasive blackberries at bay is a testament to your commitment to fostering a healthier ecosystem. By consistently applying these principles, you are playing an active role in cultivating a balanced garden environment and preserving the integrity of your cherished outdoor retreat.