Worms play a crucial role in the health and well-being of potted plants. While some worms are beneficial and contribute to soil aeration and nutrient distribution, others can be harmful and cause damage to plant roots. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the different types of worms commonly found in potted plants, their characteristics, and their impact on plant health. By understanding the types of worms in your potted plants, you can effectively manage and maintain healthy flora.
Post Summary
- Knowing the types of worms in your potted plants is essential for plant health.
- Beneficial worms, such as red wigglers and potworms, contribute to soil aeration and nutrient distribution.
- Harmful worms, like grub worms and parasite nematodes, can damage plant roots and hinder growth.
- Regular observation and appropriate potting soil can help manage worm infestations.
- Implementing control measures when necessary can create an optimal environment for your potted plants to thrive.
Red Wigglers or Earthworms
Red wigglers, also known as earthworms or Eisenia foetida, are highly beneficial for potted plants. These worms aerate the soil by creating tunnels, allowing oxygen to reach the plant roots. They also break down organic matter in the soil, releasing essential nutrients for plant growth. Red wigglers produce nutrient-rich castings, which act as a natural fertilizer. Their movements in the soil improve soil structure, leading to better water retention and drainage. When it comes to promoting optimal plant health, red wigglers are the ideal worms to have in your potted plants.
Benefits of Red Wigglers
- Soil aeration: Red wigglers create tunnels in the soil, improving its structure and allowing oxygen to reach the plant roots.
- Nutrient distribution: These worms break down organic matter, releasing nutrients that are essential for plant growth.
- Natural fertilizer: Red wiggler castings are rich in nutrients, providing plants with a natural and organic source of fertilizer.
- Improved soil structure: The movements of red wigglers in the soil improve its overall structure, leading to better water retention and drainage.
“Red wigglers are highly beneficial for potted plants as they aerate the soil, distribute nutrients, and improve soil structure.”
To ensure the presence of red wigglers in your potted plants, you can introduce them into the soil. Red wigglers are readily available for purchase at gardening stores, or you can source them from existing compost piles. Provide a suitable environment for the worms by maintaining moist soil and avoiding the use of chemical pesticides that may harm them. By incorporating red wigglers into your potted plants, you can create an optimal growing environment for healthy and thriving flora.
| Benefits of Red Wigglers | Uses of Earthworms in Potted Plants |
|---|---|
| Soil aeration | Improves soil structure |
| Nutrient distribution | Enhances water retention |
| Natural fertilizer | Promotes optimal plant growth |
Grub Worms
Grub worms, the larvae of various beetle species, can cause significant damage to your potted plants. These white, curved-shaped worms feed on plant roots and organic matter in the soil, leading to weakened root systems and poor plant health. If left unchecked, grub worm infestations can result in wilting, yellowing leaves, and even death of your plants.
Controlling grub worm infestations is crucial to protect the well-being of your potted plants. There are several methods you can employ to manage and prevent further damage from these destructive worms. One approach is to remove and discard infested soil, ensuring that you remove as many grubs as possible. This helps to reduce the population and limit their negative impact on your plants.
Applying insecticides can also be an effective way to control grub worms. Choose an appropriate insecticide that targets these specific pests and follow the instructions carefully. Additionally, introducing natural predators to your potted plants can help keep grub worm populations in check. Nematodes, predatory insects, and birds can all contribute to controlling infestations.
Regular monitoring of your plants is essential to detect grub worm infestations early on. By implementing these control measures and taking proactive steps to manage grub worms, you can protect the health and vitality of your potted plants.
Parasite Nematodes
Parasite nematodes are harmful worms that can wreak havoc on your potted plants. These microscopic pests feed on plant roots, leaves, and flowers, causing poor growth and reduced yields. If left unchecked, nematode infestations can lead to wilting, yellow leaves, stunted growth, and damaged roots.
To identify the presence of nematodes in your potted plants, closely observe the symptoms mentioned above. Additionally, carefully inspect the roots for signs of damage or discoloration. Nematodes can be difficult to spot due to their size, but taking preventive measures is vital to protect your plants.
Controlling nematode infestations requires prompt action. One approach is to spray the roots and leaves with a liquid insecticide or a diluted bleach solution to kill the worms. However, severe infestations may necessitate uprooting the affected plant and replanting it in fresh soil to prevent the spread of nematodes. Regular monitoring and early intervention are key to managing these harmful worms and ensuring the health of your potted plants.
Tips for Managing Nematode Infestations:
- Regularly inspect potted plants for symptoms of nematode infestation.
- Closely examine plant roots for signs of damage or discoloration.
- If nematodes are detected, take immediate action to control their population.
- Spray roots and leaves with a liquid insecticide or diluted bleach solution.
- In severe cases, uproot and replant affected plants in fresh soil.
- Monitor and maintain healthy growing conditions to prevent future infestations.
Remember:
“Early detection and proactive management are essential for effectively controlling nematode infestations and safeguarding the well-being of your potted plants.”
| Nematode Symptoms | Control Methods |
|---|---|
| Wilting | Spray with liquid insecticide |
| Yellow leaves | Apply diluted bleach solution |
| Stunted growth | Uproot and replant in fresh soil |
| Root damage | Regular monitoring and early intervention |
Potworms: Beneficial Worms for Your Potted Plants
Potworms, also known as enchytraeids, are tiny, white worms commonly found in both potted plants and outdoor soil. These worms may not be as well-known as red wigglers or earthworms, but they play an important role in maintaining the health of your potted plants. While potworms may not be as visually appealing as other worms, they offer a range of benefits that contribute to the overall well-being of your plants.
One of the key benefits of potworms is their ability to promote soil aeration. As they move through the soil, potworms create small tunnels, allowing air to circulate and reach the roots of your plants. This helps to prevent soil compaction and ensures that your plants receive the oxygen they need to thrive. Additionally, potworms aid in the decomposition of organic matter, breaking down dead plant material and releasing nutrients that are essential for plant growth.
While potworms are generally beneficial, it’s important to monitor their population to maintain a healthy balance in your potted plants. An excessive number of potworms can compete with other beneficial worms for nutrients, potentially causing nutrient deficiencies in your plants. To control potworm infestations, you can manually remove excess worms from the soil. Repotting your plants with fresh soil and avoiding overfeeding can also help prevent an overpopulation of potworms.
Benefits of Potworms:
- Promote soil aeration, improving oxygen flow to plant roots
- Assist in the decomposition of organic matter
- Release essential nutrients for plant growth
In conclusion, potworms are beneficial worms that contribute to the overall health of your potted plants. They help to aerate the soil and break down organic matter, creating an optimal environment for plant growth. By monitoring their population and implementing control measures when necessary, you can ensure a healthy balance and promote the well-being of your potted plants.
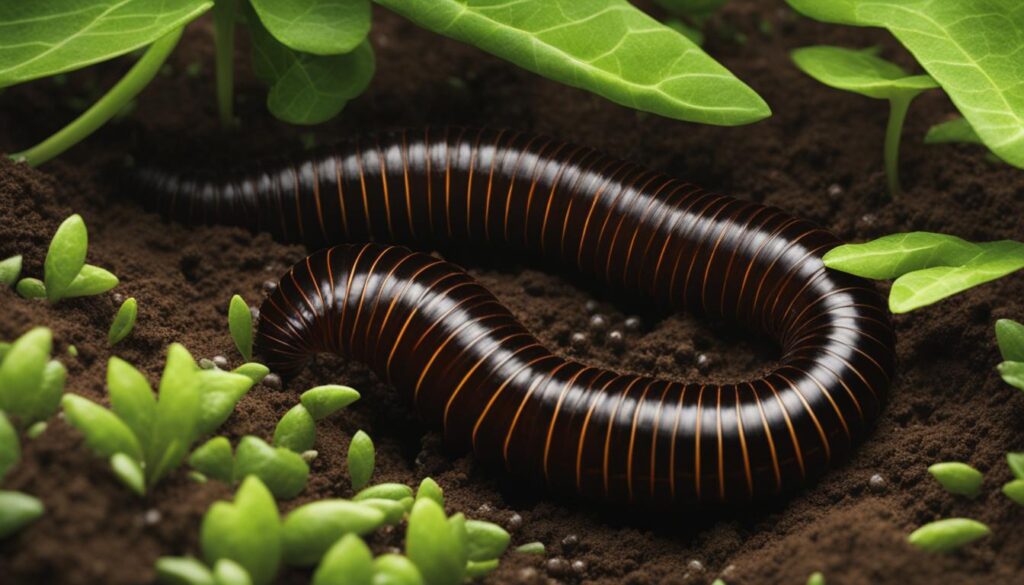
Leafminers and Millipedes
Leafminers and millipedes are two types of organisms commonly found in potted plants. While leafminers can have a negative impact on plant health, millipedes can provide several benefits for the soil. Understanding the characteristics and effects of these organisms is essential for proper plant care and maintenance.
Leafminers are pests that feed on plant leaves, causing damage and discoloration. They create unique patterns of holes on the leaf surface, resulting in wilting and hindered photosynthesis. These pests can be a nuisance in potted plants, affecting their overall appearance and health. It is important to take proactive measures to manage and control leafminers in order to minimize their impact on your plants.
On the other hand, millipedes are segmented creatures that play a beneficial role in the soil. They feed on decaying matter and help break down organic materials, contributing to the nutrient cycle in the ecosystem. Millipedes promote soil aeration and decomposition, which can improve the overall health and fertility of the soil. In moderate numbers, millipedes can be a valuable addition to your potted plants, aiding in the maintenance of a balanced and healthy soil ecosystem.
| Leafminers | Millipedes |
|---|---|
| Feed on plant leaves | Feed on decaying matter |
| Cause damage and discoloration | Contribute to soil aeration and decomposition |
| Result in wilting and hindered photosynthesis | Promote soil health and fertility |
Managing and controlling leafminers through organic pest control methods is important to prevent damage to your plants. Proper plant care, including regular inspection and prompt action when leafminer infestations are detected, can help maintain the health and vitality of your potted plants. Additionally, creating a favorable environment for millipedes can contribute to soil health and the overall well-being of your plants.
Conclusion
Understanding the types of worms in your potted plants is crucial for promoting healthy flora. Beneficial worms like red wigglers and potworms contribute to soil aeration, nutrient distribution, and the removal of harmful bacteria. These worms work tirelessly to create an optimal environment for your plants to thrive.
However, it’s important to manage worm infestations to prevent damage to your plants. Harmful worms such as grub worms and parasite nematodes can cause significant harm to plant roots and hinder growth. Regular observation and implementing control measures when necessary will help you maintain a balanced ecosystem in your potted plants.
To ensure the well-being of your plants, use appropriate potting soil and monitor the population of worms. By understanding the characteristics and impact of different worms, you can create a favorable environment for your plants to flourish. With proper care and management, you can enjoy the beauty and vitality of your potted plants for years to come.
FAQ
Are all worms beneficial for potted plants?
No, some worms can be harmful and cause damage to plant roots.
Which worms are beneficial for potted plants?
Red wigglers, also known as earthworms, are highly beneficial for potted plants. They improve soil structure, distribute nutrients, and aerate the soil.
How do red wigglers benefit potted plants?
Red wigglers aerate the soil, break down organic matter, create nutrient-rich castings, and improve water retention and drainage.
What damage can grub worms cause to potted plants?
Grub worms feed on plant roots and damage organic matter in the soil, weakening the root system and potentially causing wilting and death of the plant.
How can I control grub worm infestations?
Methods such as removing infested soil, applying insecticides, or introducing natural predators can help manage and prevent further damage from grub worms.
What are nematodes and how do they harm potted plants?
Nematodes are harmful worms that feed on plant roots, leaves, and flowers, resulting in poor plant growth, small yields, wilting, yellow leaves, stunted growth, and damaged roots.
How can I treat nematode infestations in potted plants?
Spraying roots and leaves with a liquid insecticide or bleach can help control nematode populations. Severe infestations may require uprooting and replanting with fresh soil.
What are potworms and why are they important?
Potworms are tiny, white worms that promote soil aeration, decomposition, and the removal of harmful bacteria. However, an excessive population of potworms can cause problems, so monitoring their numbers is important.
How can I control potworm infestations?
Monitoring their numbers, removing excess worms, repotting with fresh soil, and avoiding overfeeding can help control potworm infestations in potted plants.
What damage do leafminers cause to potted plants?
Leafminers feed on plant leaves, creating holes and causing wilting and hindered photosynthesis. They can damage the overall health of potted plants.
Are millipedes beneficial for potted plants?
Yes, millipedes help break down organic materials in the soil, aiding in soil aeration and decomposition. However, leafminers should be controlled to prevent damage to plants.
How can I manage and control leafminers in potted plants?
Leafminers can be managed through organic pest control methods to prevent damage to potted plants.
Are the Types of Worms in Potted Plants the Same as the Worms on Strawberry Plants?
Yes, the types of worms in potted plants are similar to the ones on strawberry plants. If you’re wondering how to remove strawberry worms, simply use a natural pesticide or neem oil to get rid of them. Be sure to check the specific recommendations for your plant type before proceeding.