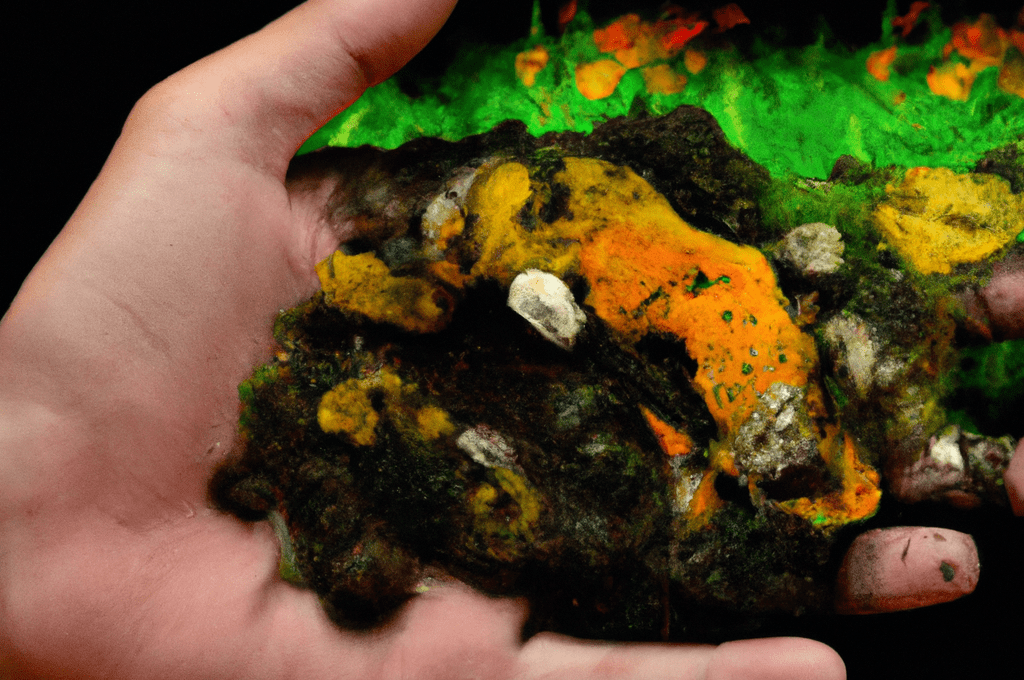
Are you interested in composting but worried about the presence of mold in your compost pile? You’re not alone. While mold can be a natural part of the composting process, it’s important to understand the potential risks and take proper safety precautions.
In this article, we’ll explore the topic of mold in compost and provide you with the information you need to make informed decisions about composting at home.
Composting is a great way to reduce waste and create nutrient-rich soil for your garden. But when it comes to mold, it’s important to be aware of the potential hazards. Moldy food can be composted, but precautions should be taken to ensure safety.
In this article, we’ll discuss the different types of mold you may encounter in your compost, the foods that are safe to compost, and the health and safety precautions you should take to protect yourself and your family.
So, let’s dive in and learn more about mold in compost: is it safe or dangerous?
Quick Summary
- Mold in compost is generally safe, but precautions should be taken.
- The composting process is about decomposition and moldy food speeds up the process.
- White mold is common in compost and indicates healthy decomposition.
- Large amounts of mold can be harmful, so wear gloves and a mask when working with compost.
What is Composting?
You can create compost by combining organic materials like fruits, vegetables, and coffee grounds, which will break down over time with the help of bacteria and fungi.
Composting benefits the environment by reducing landfill waste and creating nutrient-rich soil for gardening.
There are different types of composting methods, such as open-air piles, enclosed bins, and vermicomposting using worms.
Each method has its own benefits and drawbacks, so it’s important to choose the method that works best for your lifestyle and space.
Open-air piles are the simplest and most traditional method, but they require more space and can attract pests and animals.
Enclosed bins are a more controlled method, allowing for easier maintenance and less odor, but they require an initial investment and may not work well in extreme temperatures.
Vermicomposting is a method that uses worms to break down waste quickly and efficiently, but it requires specific conditions and may not be suitable for everyone.
Regardless of the method, composting is a simple and effective way to reduce waste and create healthy soil for plants.
Can Mold in Compost Contaminate or Harm a Garden with Excessive Mulch?
The effect of excessive mulch on gardens can be detrimental if mold in compost contaminates the soil. Mold can grow in compost that is too wet or lacks sufficient air circulation, resulting in potential harm to garden plants. Regularly monitoring compost moisture and turning it frequently helps prevent mold growth and maintain a healthy garden environment.
Food and Mold in Composting
Inspect your produce for signs of bruising and check the expiration dates on food items before adding them to your compost pile. This will help prevent mold growth and ensure the safety of your compost.
Some common food waste for composting includes fruits and vegetables, coffee grounds, bread, and grains. These items can speed up the decomposition process and provide essential nutrients for your garden.
To further reduce the risk of mold growth in your compost, it’s important to avoid adding meat, bones, fish, oils, and fats to your pile. These items can attract pests and create unpleasant odors.
Instead, consider using a bokashi composting method for moldy meats and dairy products.
Composting benefits the environment by reducing landfill waste and provides a natural way to nourish your garden.
By following these simple tips, you can safely and effectively compost your food waste.
Health and Safety Precautions
Protect yourself from harmful fungal infections by wearing safety gear when working with compost. Mold in compost may be generally safe, but it can still pose health risks if inhaled in large amounts. Aspergillosis and Histoplasmosis are two common infections caused by fungal inhalation, and they can cause serious health problems.
To avoid these risks, it’s important to wear gloves and a mask when handling organic materials in your garden. By taking these simple precautions, you can enjoy the benefits of composting without putting your health at risk.
Remember to always handle moldy foods with care, and avoid adding items like bread, meat, bones, fish, oils, and fats to your compost pile. By following these guidelines, you can create healthy, nutrient-rich soil for your garden while keeping yourself and your family safe from harmful fungal infections.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can mold in compost attract pests or rodents?
To prevent pests and rodents in your compost, follow composting best practices like burying food scraps and regularly turning your pile. Keep your compost covered and avoid adding meat, bones, or fatty foods. Mold prevention is key to avoiding attractants.
Is it safe to use compost that contains mold on edible plants?
Using moldy compost on edible plants can be risky as some molds can produce toxins harmful to humans. Prevent mold growth by adding dry materials, turning the pile, and monitoring moisture levels. The benefit of composting is reducing landfill waste and improving soil health.
How does the presence of mold affect the nutrient content of compost?
When mold grows in compost, it doesn’t affect the nutrient content. The mold growth rate depends on composting temperatures, but the compost will still provide nutrients for your plants. Take precautions and wear protective gear when handling moldy compost.
Can mold in compost cause allergic reactions in humans?
Mold allergies may occur when handling compost, but they are rare. The composting process should kill off mold, and wearing gloves and a mask can reduce the risk of allergic reactions.
Are there any types of mold that should not be present in compost?
When managing mold in compost, it’s important to note that certain types of mold should not be present. Composting techniques, such as proper moisture and airflow, can prevent harmful molds like black mold from growing.