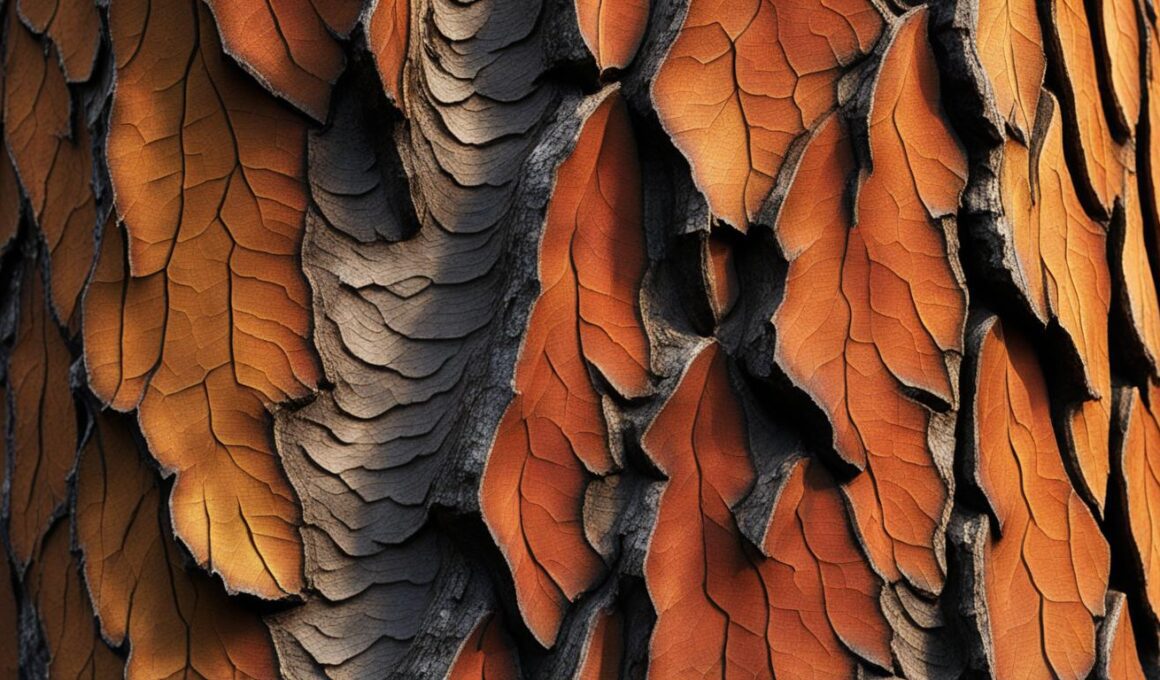
If you’ve ever come across a beautiful tree with unique bark that changes as it ages, chances are you’ve encountered a Sugar Maple tree.
The Sugar Maple, scientifically known as Acer saccharum, is a large deciduous tree native to North America. It is highly valued for its distinctive bark, which serves as a key characteristic for identifying and appreciating this magnificent tree.
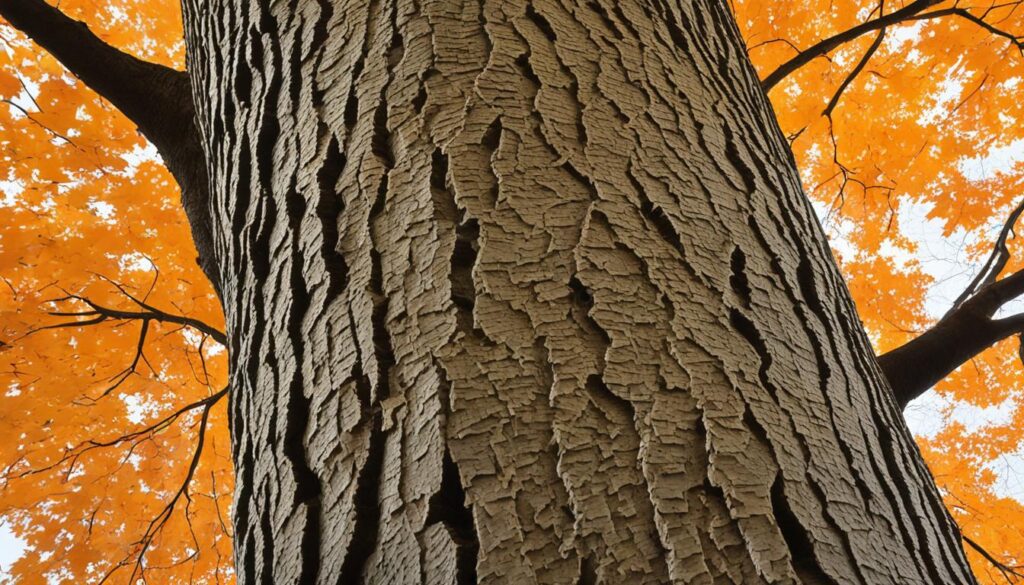
When young, the bark of the Sugar Maple is smooth and gray, giving the tree a sleek and elegant appearance. However, as it matures, the bark transforms into a scaly texture with a dark gray hue, adding depth and character to its visual appeal.
In addition to its unique bark, the Sugar Maple can be recognized by its opposite branching pattern and lobed leaves. These features, combined with its distinct bark, make it relatively easy to identify and differentiate from other tree species.
Moreover, the Sugar Maple is known by various names such as Hard Maple, Rock Maple, Head Maple, Sugartree, and Bird’s-eye Maple, reflecting its rich history and cultural significance.
This remarkable tree holds significant value beyond its aesthetic appeal. The wood of the Sugar Maple is highly sought after for its strength and durability, making it a prized material for furniture making, flooring, and paneling. Additionally, Sugar Maple trees are the primary source of maple syrup production, with their sap containing twice the sugar content of other maple species. This makes them indispensable in the maple syrup industry, contributing to their economic importance.
On an ecological level, Sugar Maple trees play a vital role by providing food and habitat for various wildlife species in their natural habitats. They are also the state tree of New York and the national tree of Canada, underscoring their cultural and historical significance.
In this article, we will delve deeper into the characteristics of Sugar Maple tree bark, helping you identify and appreciate these magnificent trees. We will also explore their cultural, economic, and ecological value, showcasing why they are cherished in American landscapes.
So, join us as we explore the captivating world of Sugar Maple tree bark and discover the wonders that lie within.
Identifying Sugar Maple Trees by Bark and Branching
One of the key features for identifying Sugar Maple trees is their bark and branching patterns. The bark of young Sugar Maple trees is smooth and gray, while mature trees have scaly and dark gray bark. This distinct bark pattern helps differentiate Sugar Maple from other maple species.
Another characteristic of Sugar Maple trees is their opposite branching pattern, where branches emerge in pairs opposite to each other on the main stem. This opposite branching combined with the distinctive bark helps in distinguishing Sugar Maple trees from other trees with similar branching patterns.
It’s important to note that not every branch on a Sugar Maple will have an opposite branch pair, as some branches may break off or fail to thrive. However, overall, the tree will have a consistent opposite branching pattern. These features make it relatively easy to identify Sugar Maple trees, even in the absence of leaves.
Uses and Value of Sugar Maple Trees
Sugar Maple trees have significant uses and value both economically and ecologically. The wood of Sugar Maple trees is highly valued for its strength and durability, making it ideal for various applications. It is commonly used in furniture making, flooring, paneling, and even musical instruments. The unique grain patterns, such as birdseye maple, curly maple, and fiddleback maple, are highly sought after in the woodworking industry, adding distinct beauty to crafted items.
In addition to its wood value, Sugar Maple trees are also widely recognized as the primary source of maple syrup production. The sap of Sugar Maple trees possesses twice the sugar content compared to other maple species, making it an ideal choice for syrup production. This flavorful and natural sweetener is used in a variety of dishes, desserts, and beverages. Maple syrup production is a thriving industry in the United States and Canada, contributing significantly to the local and national economies. Vermont, known as the “Maple Syrup Capital,” is the largest producer of maple syrup in the US.
Aside from its economic value, Sugar Maple trees are ecologically important. They provide food and habitat for various wildlife species, including deer, squirrels, and birds. The dense canopy of Sugar Maple trees offers shelter and nesting sites, supporting healthy ecosystems and biodiversity. Moreover, the brilliant fall foliage of Sugar Maple trees adds aesthetic value to landscapes, transforming them into vibrant spectacles of red, orange, and yellow hues. The iconic beauty of Sugar Maple trees contributes to the breathtaking colors and scenic views witnessed during the autumn season.
In summary, Sugar Maple trees offer a wide range of uses and possess substantial value both economically and ecologically. From their highly prized wood to their crucial role in maple syrup production and ecological biodiversity, Sugar Maple trees enrich our lives in numerous ways. Appreciating the economic and ecological importance of Sugar Maple trees is vital for understanding their significance in the American landscape.
Sugar Maple Tree Bark Conclusion
In conclusion, the distinctive features of Sugar Maple tree bark make it easy to identify these iconic trees. The smooth and gray bark of young Sugar Maple trees transforms into scaly and dark gray bark as they mature. This unique bark pattern, along with the opposite branching pattern and lobed leaves, sets Sugar Maple trees apart from other species.
Not only are Sugar Maple trees visually appealing, but they also hold significant economic and ecological value. The wood of Sugar Maple trees is highly valued for its strength and durability, making it ideal for various woodworking purposes, including furniture making. Additionally, Sugar Maple trees are the primary source of maple syrup production, as their sap contains twice the sugar content of other maple species.
Furthermore, Sugar Maple trees play a vital role in ecosystems by providing food and habitat for a range of wildlife species. Their brilliant fall foliage adds aesthetic value to landscapes, contributing to the vibrant colors observed during autumn. Understanding and appreciating the features of Sugar Maple tree bark is essential for tree identification and to fully grasp their value in American landscapes.
What are the unique features of sugar maple tree bark and how does it differ from caring for a braided hibiscus tree?
The sugar maple tree bark is known for its unique, deeply furrowed texture, while the braided hibiscus tree has a smooth, light-colored bark. When it comes to caring for a braided hibiscus tree, regular watering, good drainage, and occasional pruning are essential. For more braided hibiscus tree care tips, consult a professional.